| Brand Brand name of the company that manufactures the device. | Samsung |
| Model Model name of the device. | Galaxy Tab S3 |
| Model alias Аlternative names, under which the model is known. | SM-T825 T825 SM-T827V T827V |
- Mobile Phones In India
- S3 Graphics Mobile Phones Unlocked
- S3 Graphics Mobile Phones Verizon
- Mobile Phones Wikipedia
Design
Information about the dimensions and weight of the device, shown in different measurement units. Body materials, available colors, certifications.
HTC Purchases S3 Graphics—It's More Important Than You Think VIA announced today that it's signed an agreement to sell its share in S3 Graphics to the mobile phone manufacturer HTC.
Jul 06, 2011 In addition to its traditional markets in PCs and game consoles, S3 Graphics’ texture compression technology is increasingly being applied to smartphones and tablets, HTC said in a statement. S3 is responsible for graphics that you see all over the place. This company has developed visualization graphics or computers, mobile devices and even gaming consoles. Once the proposed deal goes through all of the regulatory proceedings, HTC will instantly be given access to their stash of patents as well as the companies’ full workforce.
Mobile Phones In India
- Smartphone vendor High Tech Computer (HTC) will acquire graphics chip maker S3 Graphics for US$300 million, strengthening its patent portfolio in the process. With the acquisition, HTC will obtain.
- 48MP Sony IMX586 Dual Camera, 20MP Sony IMX376 Front Camera, Helio P70 Masterful AI Processor, 6GB RAM + 128GB ROM. 5150mAh Powerful Battery,18W Fast Charging & NFC. 6.3' FHD+ Waterdrop Full Screen,2340.1080 In-cell, LTPS Display. Luxury Ceramic Design, Stock Android 9 Pie. Package contents.
| Width Information about the width, i.e. the horizontal side of the device when it is used in its standard orientation. | 237.3 mm (millimeters) 23.73 cm (centimeters) 0.779 ft (feet) 9.343 in (inches) |
| Height Information about the height, i.e. the vertical side of the device when it is used in its standard orientation. | 169 mm (millimeters) 16.9 cm (centimeters) 0.554 ft (feet) 6.654 in (inches) |
| Thickness Information about the thickness/depth of the device in different measurement units. | 6 mm (millimeters) 0.6 cm (centimeters) 0.02 ft (feet) 0.236 in (inches) |
| Weight Information about the weight of the device in different measurement units. | 434 g (grams) 0.96 lbs (pounds) 15.31 oz (ounces) |
| Volume Estimated volume of the device, calculated from the dimensions provided by the manufacturer. Applies for devices in the form of a rectangular parallelepiped. | 240.62 cm³ (cubic centimeters) 14.61 in³ (cubic inches) |
| Colors Information about the colors, in which the device is available in the market. | Black Silver |
| Body materials Materials used in the fabrication of the device's body. | Metal Glass |
| SIM card type Information about the type and size (form factor) of the SIM card used in the device. | Nano-SIM (4FF - fourth form factor, since 2012, 12.30 x 8.80 x 0.67 mm) |
| Number of SIM cards Information about the number of SIM cards, supported by the device. | 1 |
Networks
A mobile (cellular) network is a radio system, which allows a large number of mobile devices to communicate with each other.
| GSM GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) was developed to replace the analog cellular network (1G), therefore it is referred to as a 2G mobile network. It has been improved with the addition of General Packet Radio Services (GPRS) and later via the Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE) technology. | GSM 850 MHz GSM 900 MHz GSM 1800 MHz GSM 1900 MHz |
| UMTS UMTS stands for Universal Mobile Telecommunications System. Based on the GSM standard, it is deemed as a 3G mobile network standard. It has been developed by the 3GPP and its major advantage is the provision of greater bandwidth and spectral efficiency, due to the W-CDMA technology. | UMTS 850 MHz UMTS 900 MHz UMTS 1900 MHz UMTS 2100 MHz |
| LTE LTE is deemed to be the fourth generation (4G) of mobile communications technology. It has been developed by the 3GPP based on the GSM/EDGE and UMTS/HSPA technologies in order to increase the speed and capacity of wireless data networks. A further development of the technology is called LTE Advanced. | LTE 700 MHz Class 13 LTE 700 MHz Class 17 LTE 800 MHz LTE 850 MHz LTE 900 MHz LTE 1700/2100 MHz LTE 1800 MHz LTE 1900 MHz LTE 2100 MHz LTE 2600 MHz LTE-TDD 2300 MHz (B40) LTE 700 MHz (B28) |
| Mobile network technologies There are several network technologies that enhance the performance of mobile networks mainly by increased data bandwidth. Information about the communication technologies supported by the device and their respective uplink and downlink bandwidth. | UMTS (384 kbit/s ) EDGE GPRS HSPA+ LTE Cat 6 (51.0 Mbit/s , 301.5 Mbit/s ) |
Operating system
Operating system is the system software, which manages and controls the functioning of the hardware components of the device.
| Operating system (OS) Information about the operating system used by the device as well as its version. | Android 7.0 Nougat Androd 8.0 Oreo |
| SoC The SoC integrates different hardware components such as the CPU, GPU, memory, peripherals, interfaces, etc., as well as software for their functioning. | Qualcomm Snapdragon 820 MSM8996 |
| Process technology Information about the process technology used in manufacturing the chip. The value in nanometers represents half the distance between elements that make up the CPU. | 14 nm (nanometers) |
| CPU CPU is the Central Processing Unit or the processor of a mobile device. Its main function is to interpret and execute instructions contained in software applications. | 2x 2.15 GHz Kryo, 2x 1.6 GHz Kryo |
| CPU bits The CPU bits are determined by the bit-size of the processor registers, address buses and data buses. 64-bit CPUs provide better performance than 32-bit ones, which on their part perform better than 16-bit processors. | 64 bit |
| Instruction set The instruction set architecture (ISA) is a set of commands used by the software to manage the CPU's work. Information about the set of instructions the processor can execute. | ARMv8-A |
| Level 1 cache memory (L1) The cache memory is used by the processor in order to shorten the time needed to access data and instructions that a frequently used. The L1 (level 1) cache memory has a small volume, but operates faster than the RAM and the rest cache memory levels. If the processor does not find the data needed in L1, it continues to look for it in the L2 cache memory. In some processors the search in L1 and L2 is simultaneous. | 32 KB + 32 KB (kilobytes) |
| Level 2 cache memory (L2) The L2 (level 2) cache memory is slower than L1, but has a larger capacity, instead, which allows it to cache more data. Just like L1, it is much faster than the system memory (RAM). If the CPU does not find the data needed in L2, it proceeds to look for them in the L3 cache memory (if there is such) or in the RAM. | 1536 KB (kilobytes) 1.5 MB (megabytes) |
| CPU cores A CPU core is the processor unit, which executes software instructions. Presently, besides single-core processors, there are dual-core, quad-core, hexa-core and so on multi-core processors. They increase the performance of the device allowing the execution of multiple instructions in parallel. | 4 |
| CPU frequency The frequency of the processor describes its clock rate in cycles per second. It is measured in Megahertz (MHz) or Gigahertz (GHz). | 2150 MHz (megahertz) |
| GPU GPU is a graphical processing unit, which handles computation for 2D/3D graphics applications. In mobile devices GPU is usually utilized by games, UI, video playback, etc. GPU can also perform computation in applications traditionally handled by the CPU. | Qualcomm Adreno 530 |
| GPU frequency The frequency is the clock rate of the graphic processor (GPU), which is measured in Megahertz (MHz) or Gigahertz (GHz). | 624 MHz (megahertz) |
| RAM capacity RAM (Random-Access Memory) is used by the operating system and all installed applications. Data in the RAM is lost after the device is turned off or restarted. | 4 GB (gigabytes) |
| RAM type Information about the type of RAM used by the device. | LPDDR4 |
| RAM channels Information about the number of RAM channels integrated in the SoC. More channels mean higher data transfer rates. | Double channel |
| RAM frequency RAM frequency relates directly to the rate of reading/writing from/in the RAM memory. | 1866 MHz (megahertz) |
Storage
Every mobile device has a built-in storage (internal memory) with a fixed capacity.
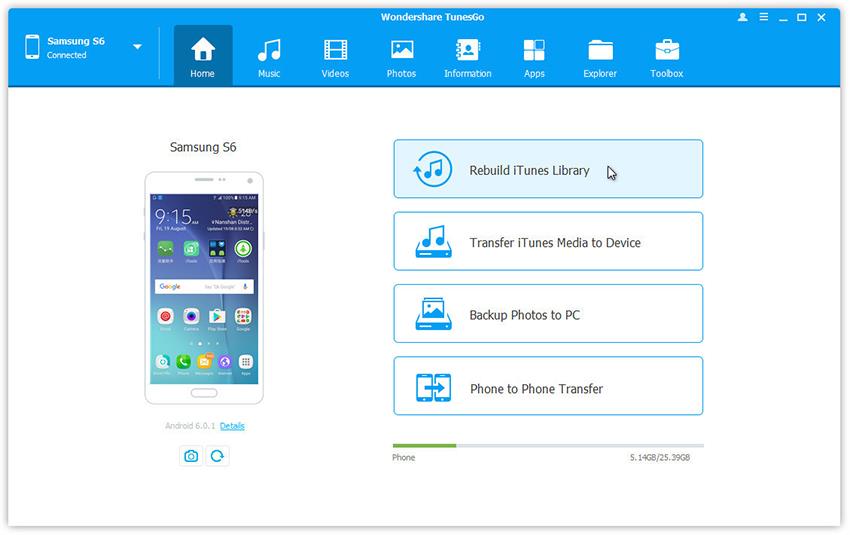
| Storage Information about the capacity of the built-in storage of the device. Sometimes one and the same model may is offered in variants with different internal storage capacity. | 32 GB (gigabytes) |
| Types The various types of memory cards are characterized by different sizes and capacity. Information about the supported types of memory cards. | microSD microSDHC microSDXC |
Display
The display of a mobile device is characterized by its technology, resolution, pixel density, diagonal length, color depth, etc.
| Type/technology One of the main characteristics of the display is its type/technology, on which depends its performance. | Super AMOLED |
| Diagonal size In mobile devices display size is represented by the length of its diagonal measured in inches. | 9.7 in (inches) 246.38 mm (millimeters) 24.64 cm (centimeters) |
| Width Approximate width of the display | 7.76 in (inches) 197.1 mm (millimeters) 19.71 cm (centimeters) |
| Height Approximate height of the display | 5.82 in (inches) 147.83 mm (millimeters) 14.78 cm (centimeters) |
| Aspect ratio The ratio between the long and the short side of the display | 1.333:1 4:3 |
| Resolution The display resolution shows the number of pixels on the horizontal and vertical side of the screen. The higher the resolution is, the greater the detail of the displayed content. | 2048 x 1536 pixels |
| Pixel density Information about the number of pixels per centimeter (ppcm) or per inch (ppi) of the display. The higher the pixel density, the more detailed and clearer is the information displayed on the screen. | 264 ppi (pixels per inch) 103 ppcm (pixels per centimeter) |
| Color depth The color depth of the display is also known as bit depth. It shows the number of bits used for the color components of one pixel. Information about the maximum number of colors the screen can display. | 24 bit 16777216 colors |
| Display area The estimated percentage of the screen area from the device's front area. | 72.89 % (percent) |
| Other features Information about other functions and features of the display. | Capacitive Multi-touch |
| Sensors Sensors vary in type and purpose. They increase the overall functionality of the device, in which they are integrated. | Proximity Light Accelerometer Compass Gyroscope Fingerprint Hall |
Rear camera
The primary camera of the mobile device is usually placed on its back and can be combined with one or more additional cameras.
| Sensor type Information about the sensor type of the camera. Some of the most widely used types of image sensors on mobile devices are CMOS, BSI, ISOCELL, etc. | CMOS BSI (backside illumination) |
| Aperture The aperture (f-stop number) indicates the size of the lens diaphragm opening, which controls the amount of light reaching the image sensor. The lower the f-stop number, the larger the diaphragm opening is, hence, the more light reaches the sensor. Usually, the f-stop number specified is the one that corresponds to the maximum possible diaphragm opening. | f/1.9 |
| Focal length and 35 mm equivalent Focal length is the distance in millimeters from the focal point of the image sensor to the optical center of the lens. The 35 mm equivalent indicates the focal length at which a full-frame camera will achieve an angle of view that's the same as the one of the camera of the mobile device. It is measured by multiplying the native focal length of the camera by the crop factor of the sensor. The crop factor itself can be determined as the ratio between the diagonal distances of the image sensor in the 35 mm camera and a given sensor. | 27 mm (millimeters)*(35 mm / full frame) |
| Flash type The rear cameras of mobile devices use mainly a LED flash. It may arrive in a single, dual- or multi-light setup and in different arrangements. | LED |
| Image resolution One of the main characteristics of the cameras is their image resolution. It states the number of pixels on the horizontal and vertical dimensions of the image, which can also be shown in megapixels that indicate the approximate number of pixels in millions. | 4160 x 3120 pixels 12.98 MP (megapixels) |
| Video resolution Information about the maximum resolution at which the rear camera can shoot videos. | 3840 x 2160 pixels 8.29 MP (megapixels) |
| Video FPS Information about the maximum number of frames per second (fps) supported by the rear camera while recording video at the maximum resolution. Some of the main standard frame rates for recording and playing video are 24 fps, 25 fps, 30 fps, 60 fps. | 30 fps (frames per second) |
| Features Information about additional software and hardware features of the rear camera which improve its overall performance. | Autofocus Continuous shooting Digital zoom Geotagging Panorama HDR Touch focus Face detection White balance settings ISO settings Exposure compensation Self-timer Scene mode |
| Sensor type Information about the sensor type of the camera. Some of the most widely used types of image sensors on mobile devices are CMOS, BSI, ISOCELL, etc. | CMOS BSI (backside illumination) |
| Aperture The aperture (f-stop number) indicates the size of the lens diaphragm opening, which controls the amount of light reaching the image sensor. The lower the f-stop number, the larger the diaphragm opening is, hence, the more light reaches the sensor. Usually, the f-stop number specified is the one that corresponds to the maximum possible diaphragm opening. | f/2.2 |
| Focal length and 35 mm equivalent Focal length is the distance in millimeters from the focal point of the image sensor to the optical center of the lens. The 35 mm equivalent indicates the focal length at which a full-frame camera will achieve an angle of view that's the same as the one of the camera of the mobile device. It is measured by multiplying the native focal length of the camera by the crop factor of the sensor. The crop factor itself can be determined as the ratio between the diagonal distances of the image sensor in the 35 mm camera and a given sensor. | 23 mm (millimeters)*(35 mm / full frame) |
| Image resolution Information about the number of pixels on the horizontal and vertical dimensions of the photos taken by the front camera, indicated in megapixels as well. | 2592 x 1944 pixels 5.04 MP (megapixels) |
| Video resolution Information about the maximum resolution of the videos shot by the front camera. | 1920 x 1080 pixels 2.07 MP (megapixels) |
| Video FPS Digital cameras are able to shoot videos at different frames per second (fps). Some of the main standard frame rates for recording and playing video are 24 fps, 25 fps, 30 fps, 60 fps. Information about the maximum possible fps for shooting videos at the maximum possible resolution. | 30 fps (frames per second) |
S3 Graphics Mobile Phones Unlocked
Audio
Information about the type of speakers and the audio technologies supported by the device.
| Speaker The loudspeaker is a device, which reproduces various sounds such as ring tones, alarms, music, voice calls, etc. Information about the type of speakers the device uses. | Loudspeaker Stereo speakers |
| 4x speakers |
| Radio Information whether the device has an FM radio receiver or not. | No |
Tracking/Positioning
Information about the positioning and navigation technologies supported by the device.
| Tracking/Positioning The tracking/positioning service is provided by various satellite navigation systems, which track the autonomous geo-spatial positioning of the device that supports them. The most common satellite navigation systems are the GPS and the GLONASS. There are also non-satellite technologies for locating mobile devices such as the Enhanced Observed Time Difference, Enhanced 911, GSM Cell ID. | GPS A-GPS GLONASS BeiDou |
| Wi-Fi Wi-Fi communication between devices is realized via the IEEE 802.11 standards. Some devices have the possibility to serve as Wi-Fi Hotspots by providing internet access for other nearby devices. Wi-Fi Direct (Wi-Fi P2P) is another useful standard that allows devices to communicate with each other without the need for wireless access point (WAP). | 802.11a (IEEE 802.11a-1999) 802.11b (IEEE 802.11b-1999) 802.11g (IEEE 802.11g-2003) 802.11n (IEEE 802.11n-2009) 802.11n 5GHz 802.11ac (IEEE 802.11ac) Dual band Wi-Fi Hotspot Wi-Fi Direct |
| MiMO |
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a standard for secure wireless data transfer between different types of devices over short distances.
| Version The technology has several versions, which improve the connection speed, range, connectivity and discoverability of the devices. Information about the Bluetooth version of the device. | 4.2 |
| Features Bluetooth uses various profiles and protocols related to faster exchange of data, energy saving, better device discoverability, etc. Some of those supported by the device are listed here. | A2DP (Advanced Audio Distribution Profile) LE (Low Energy) |
| Connector type There are several USB connector types: the Standard one, the Mini and Micro connectors, On-The-Go connectors, etc. Type of the USB connector used by the device. | USB Type-C |
| Version There are several versions of the Universal Serial Bus (USB) standard: USB 1.0 (1996), the USB 2.0 (2000), the USB 3.0 (2008), etc. With each following version the rate of data transfer is increased. | 3.1 |
| Features Тhe USB interface in mobile devices may be used for different purposes such as battery charging, using the device as a mass storage, host, etc. | Charging Mass storage On-The-Go |
Headphone jack
The headphone jack is an audio phone connector, a.k.a. an audio jack. The most widely used one in mobile devices is the 3.5 mm headphone jack.
| Headphone jack Information whether the device is equipped with a 3.5 mm audio jack. | Yes |
| Connectivity Information about some of the most widely used connectivity technologies supported by the device. | Computer sync OTA sync Tethering ANT+ |
Browser
A web browser is a software application for accessing, fetching, displaying and navigating through information on the World Wide Web.
| Browser Information about some of the features and standards supported by the browser of the device. | HTML HTML5 CSS 3 |
| Audio file formats/codecs List of some of the most common audio file formats and codecs supported standardly by the device. | AAC (Advanced Audio Coding) AAC+ / aacPlus / HE-AAC v1 eAAC+ / aacPlus v2 / HE-AAC v2 FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec, .flac) MIDI MP3 (MPEG-2 Audio Layer II, .mp3) OGG (.ogg, .ogv, .oga, .ogx, .spx, .opus) WMA (Windows Media Audio, .wma) WAV (Waveform Audio File Format, .wav, .wave) |
Video file formats/codecs
Mobile devices support various video file formats and codecs, which respectively store and code/decode digital video data.
| Video file formats/codecs List of some of the most common video file formats and codecs supported standardly by the device. | 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project, .3gp) H.263 H.264 / MPEG-4 Part 10 / AVC video H.265 / MPEG-H Part 2 / HEVC MP4 (MPEG-4 Part 14, .mp4, .m4a, .m4p, .m4b, .m4r, .m4v) VC-1 VP8 WMV7 (Windows Media Video 7, .wmv) WMV8 (Windows Media Video 8, .wmv) |
| Capacity The capacity of a battery shows the maximum charge, which it can store, measured in mili-Ampere hours. | 6000 mAh (milliampere-hours) |
| Type The battery type is determined by its structure and more specifically, by the chemicals used in it. There are different battery types and some of the most commonly used in mobile devices are the lithium-ion (Li-Ion) and the lithium-ion polymer battery (Li-Polymer). | Li-Polymer |
| Features Information about some additional features of the device's battery. | Fast charging Non-removable |
| Battery life - up to 12 h |
Specific Absorption Rate (SAR)
The SAR rating shows the amount of electromagnetic radiation absorbed by the human body when using a mobile device, expressed in W/kg.
S3 Graphics Mobile Phones Verizon

| Body SAR (EU) This SAR rating shows the highest level of exposure to electromagnetic radiation measured when the device is placed at the hip level. The top SAR value for mobile devices used in Europe is limited to 2 W/kg per 10 g of tissue. This standard follows the ICNIRP Guidelines 1998 as well as the IEC standards and is determined by the CENELEC. | 0.993 W/kg (watts per kilogram) |
| Body SAR (USA) The SAR body rating shows the maximum level of exposure to electromagnetic radiation when the device is positioned against the body at the hip. The highest SAR value of mobile devices allowed in the US is set to 1.6 W/kg per 1 g of tissue. It is specified by the FCC and the CTIA follows whether the mobile devices comply with this standard. | 1.1 W/kg (watts per kilogram) |
Mobile Phones Wikipedia
| Additional features Information about other features of the device. | S Pen stylus (4096 pressure levels) |
- Try out the Savage 4 Chipset Driver for Windows 2000.
- November 30, 2000
- Windows 2000
- 724 KB
- Download the latest drivers for your S3 ProSavageDDR card.
- June 17, 2003
- Windows 2000/XP
- 4.7 MB
- January 13, 2004
- Windows 95/98/Me
- 5.4 MB
- Operating system support: Windows 2000/XP.
- June 3, 2004
- Windows 2000/XP
- 5.1 MB
- Archive for the latest S3 ProSavageDDR drivers we could find.
- September 2, 2004
- Windows 2000/XP
- 5.0 MB
- Microsoft Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows XP TabletPC Edition.
- September 2, 2004
- Windows 2000/XP
- 5.0 MB
- Windows NT 3.
- October 25, 1996
- Windows NT
- 279 KB
- Trio32 (732) & Trio64 (764) Drivers.
- August 29, 1997
- Windows NT
- 178 KB
- Binary-ViRGE Win NT 4.
- May 18, 1998
- Windows NT
- 172 KB
- Binary-ViRGE Win 95 MS Logo'd v.
- May 18, 1998
- Windows 95/98/Me
- 267 KB
- Binary-Trio 3D Win 95/98 MS Logo'd v.
- September 17, 1998
- Windows 95/98/Me
- 422 KB
- Binary MXC Win 9x v 5.
- November 4, 1998
- Windows 95/98/Me
- 412 KB
- Binary- MS Cert.
- May 13, 1999
- Windows 95/98/Me
- 244 KB
- S3 Windows 2000 beta display driver v.
- June 13, 2000
- Windows 2000/XP
- 190 KB
- S3 Windows 9x Beta Display Driver v.
- June 30, 2000
- Windows 95/98/Me
- 462 KB
- S3 Windows NT 3.
- July 13, 2000
- Windows NT
- 145 KB
- July 13, 2000
- Windows 2000/XP
- 190 KB
- April 9, 2002
- Windows 2000
- 858 KB
- April 25, 2002
- Windows 2000
- 858 KB
- April 25, 2002
- Windows XP
- 991 KB
- May 31, 2002
- Windows XP
- 993 KB
- Logo'd: SavageMX Windows 95, 98, and ME version 7.
- November 7, 2002
- Windows 95/98/Me
- 1.1 MB
- Download the latest driver for your S3 Graphics ProSavageDDR card.
- July 15, 2003
- Windows 95/98/Me
- 5.1 MB
- October 15, 2003
- Windows 2000/XP
- 4.4 MB
- S3 Trio32 (732) & S3 Trio64 (764) Drivers.
- June 16, 1997
- Windows 95/98/Me
- 167 KB
- June 30, 2000
- Windows 2000/XP
- 767 KB
- Download the latest server drivers for your S3 Graphics Savage 4 (394-398) graphics card.
- March 10, 2003
- Windows 2000/XP
- 235 KB
- The ProSavageDDR graphics controllers were included with VIA NorthBridge chipsets.
- March 28, 2006
- Windows 2000/XP
- 5.1 MB
- The ProSavageDDR graphics controllers were included with VIA NorthBridge chipsets.
- March 28, 2006
- Windows 95/98/Me
- 5.4 MB
- July 13, 2000
- Windows NT
- 205 KB
- July 13, 2000
- Windows 95/98/Me
- 453 KB
- April 21, 2005
- Windows XP 64-bit
- 9.6 MB
- April 14, 2005
- Windows 2000/XP
- 8.4 MB
- July 3, 2007
- Windows Vista 64-bit
- 11.7 MB
- July 3, 2007
- Windows Vista
- 11.4 MB
- January 20, 2006
- Windows XP 64-bit
- 13.7 MB
- October 22, 2007
- Windows 2000/XP
- 10.2 MB
- March 4, 2008
- Windows Vista 64-bit
- 12.8 MB
- March 4, 2008
- Windows Vista
- 12.3 MB
- January 20, 2006
- Windows XP 64-bit
- 13.7 MB
- March 4, 2008
- Windows 2000/XP
- 10.8 MB
- October 30, 2009
- Linux
- 5.7 MB
- March 31, 2010
- Windows 7
- 20.7 MB
- March 31, 2010
- Windows 7 64-bit
- 15.1 MB
- March 31, 2010
- Windows Vista
- 15.1 MB
- March 31, 2010
- Windows Vista 64-bit
- 20.7 MB
- March 31, 2010
- Windows XP
- 15.1 MB
- January 28, 2010
- Windows 7
- 15.2 MB
- January 28, 2010
- Windows 7 64-bit
- 20.9 MB
- January 28, 2010
- Windows Vista
- 15.2 MB
